Python tuple method
Python tuple method are ordered collections in Python that are similar to lists but with one key difference: they are immutable, meaning their elements cannot be modified after creation. While tuples don’t have as many built-in methods as lists, they do have some useful methods and operations that you can use. Here are some commonly used methods for working with tuples:
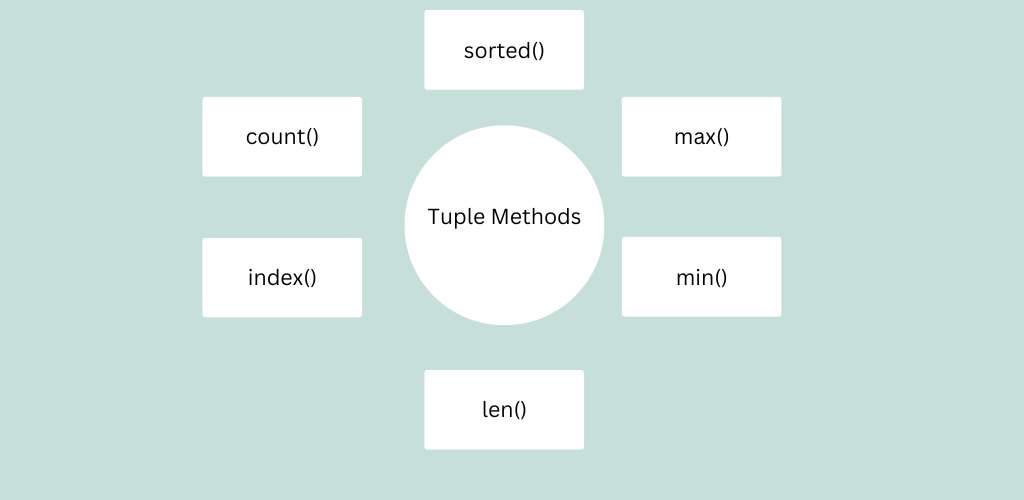
Table of Contents
count()
This method is used to count the number of occurrences of a specific element within a tuple
my_tuple = (1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 2, 5)
count_of_2 = my_tuple.count(2)
print(count_of_2) # Output: 3
index()
The index() method is used to find the index (position) of the first occurrence of a specified element
my_tuple = (10, 20, 30, 40, 50)
index_of_30 = my_tuple.index(30)
print(index_of_30) # Output: 2 (because 30 is at index 2)
len()
Although not a method specific to tuples (it works with any sequence), len() can be used to determine the length (number of elements) in a tuple
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
length = len(my_tuple)
print(length) # Output: 5
max() and min()
max() and min(): You can use these functions to find the maximum and minimum elements in a tuple
my_tuple = (10, 20, 5, 45, 30)
maximum = max(my_tuple)
minimum = min(my_tuple)
print(maximum, minimum) # Output: 45 5
sorted()
my_tuple = (3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5)
sorted_list = sorted(my_tuple)
print(sorted_list) # Output: [1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 9]
Remember that since tuples are immutable, these methods do not modify the original tuple but return new values or data as appropriate